"Tight Hamstrings, The Epidemic That Never Existed."
-Dr. Erson Religioso, DPT
 |
| Trying to touch my toes at my first SFMA seminar. |
This little nugget of knowledge developed during a conversation that my good friend Dr. E of The Manual Therapist and I were having together after his recent post. It is crazy how many times you will hear people mention how tight their "hammies" are or how often you can look at people exercising in public and the only thing they stretch is their hamstring group after some light arm circles. It is bewildering to me sometimes.
I think there is a real epidemic in progress and is growing at an exponential rate. However, the epidemic is NOT hamstring tightness...The real epidemic is a plethora of people, old and young alike, that can not touch their toes. Touching your toes without bending your knees is...or should be a fundamental human movement pattern. I know many of us fear lumbar motion and especially extreme lumbar flexion but spinal (that includes lumbar) motion is completely normal and necessary. We aren't talking about lumbar flexion under load here.
On top of the population of people that can not touch their toes...there are plenty of people that can do so. However, I didn't say everyone that could do this was able to do it satisfactorily. Using the Selective Functional Movement Assessment (SFMA) standards a person should be able to touch their toes without bending the knees, should have a uniform spinal curve throughout all of the spinal segments, have a sacral angle of > 70 degrees, and should utilize a posterior weight shift or hip hinge to achieve this goal. An inability to achieve this pattern satisfactorily represents an inability for athletic movements such as the deadlift, and an inability to reflexively stabilize the spine.
So what does this have to do with hamstrings? Most people that can not touch their toes often jump the gun and assume that it is due to posterior chain tightness or tight hamstrings. In reality, this is rarely the case. In fact, I would recommend you always get a second opinion or never evaluate yourself. I actually made this mistake myself and it was evident in a previous post where I did an SFMA video of my own multi-segmental flexion (toe touch pattern). I was wrong in my assessment and I actually had a core stability/motor control dysfunction.
So lets find out where I went wrong really quick to showcase how you can check to see if your hamstrings are tight or not.
Step 1. Check to see if toes can be touched. If not, continue on.
Why can't I? We don't know. Don't blame the hamstrings yet.Step 2. Remove Parts and Compare Left to Right.
Here I unweight one of my legs and check for change. Nothing. Continue on. Still not the hamstrings.
Step 3. Long Sitting Test - Unload body parts.
Now the hips and below will not be bearing weight and only the spine will be partially loaded against gravity. Still can't touch the toes? Continue on. (Still not the hamstrings despite my P.E. teachers scolding me for my tight hamstrings as a kid)
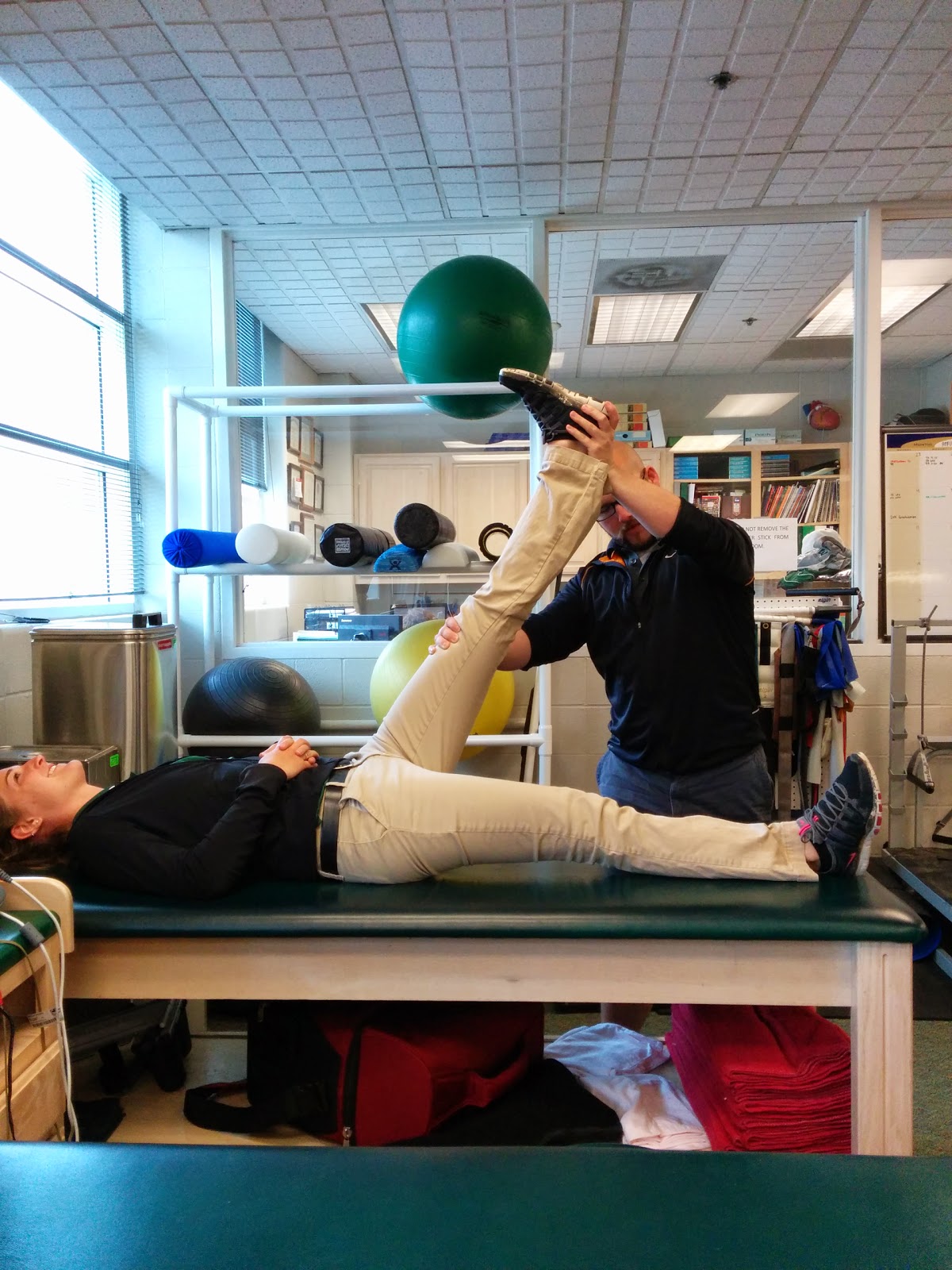
Step 4. Unload More, Check Left to Right, and begin Active versus. Passive Comparison.
In this test you are looking for & 70 degrees of hip flexion with both knees remaining straight, feet dorsiflexed, and hips neutral. An inability here STILL is not due to tight hamstrings.
Step 5. Checking Passive Motion compared with Active Motion from the previous step.
An inability here to increase motion here beyond what you achieved actively = Ding. Ding. Ding. Winner Winner, Chicken Dinner. You DO have tight hamstrings! There are a few more steps you may take after this finding to pinpoint where the mobility dysfunction is located. However, If you increase more than 10 degrees compared to active but still do not reach normal hip flexion (now 80 degrees instead of 70) then you have a mobility and stability/motor control dysfunction present! If you find that you go from ~40 degrees to normal like I do below then you sir...DO NOT HAVE TIGHT HAMSTRINGS. You have a stability/motor control dysfunction. Continue on to step 6.
Step 6. Now you must find out how poor your motor control deficit is.
To pinpoint this you regress yourself to the most basic form of stability and motor control...rolling around on the ground. If you can not roll from supine to prone with each of your different limbs then you have a primitive motor control dysfunction. Restoring the ability to roll may fix your inability to touch your toes. However, at this point we are encroaching on the area of the 4x4 matrix of the SFMA. If you aren't in pain currently then I would recommend you finding an FMS certified professional and get screened and start with working on your most dysfunctional issues there first. |
| Look at me now...Just a tiny bend in the knees. Working on it. No hamstring stretching needed. |
In conclusion, don't evaluate yourself and if you do...Get it rechecked by another set of eyes. The plumbers pipes always leak. Don't be that plumber. Secondly, practice your systems of evaluation or assessment if you have one so you can own it. If you don't use a system how can you be sure you aren't throwing spaghetti against the fridge and hoping that something sticks? What are your metrics for improvement? It has been said a million times and I'll repeat it. You do not need to use these metrics but you should be using something to set a baseline, intervene, and then compare to baseline to check for change.

















.gif)
.JPG)

